Ontoforce
 As a start-up with limited resources to devote to R&D, Ontoforce connected with iMinds’ IDLab for help reinventing the search paradigm by developing a federated search solution. The next challenge was to establish a set of data service endpoints — expanding the engine’s search territory beyond just the public web. Because Ontoforce’s solution targeted the biomedical sector, access to university research databases was key. Harvard’s Eagle-i, together with IDLab’s RML stepped in to help on that front. The DISQOVER platform that Ontoforce jointly developed further with IDLab filters and disambiguates query results to add meaning to the data it serves up to users. If a researcher wants to know what diseases are the subject of phase-three clinical trials in, e.g., California, DISQOVER blazes through the network and isolates exactly that information, presenting it graphically in a clean interface that’s easy to understand and manipulate — along with all the relevant links back to the original data. Even the interface is part of the semantic process, bringing extra meaning to displayed data. The Ontoforce solution underscores the importance of collaboration in innovation. iMinds’ IDLab helped federating the search; Harvard’s Eagle-i with IDLab’s RML ensured the data was 5-star quality; and the DISQOVER platform makes sense of it all, “semantifying” the search for users. As a result of this joint collaboration, Ontoforce’s CEO says DISQOVER can scale like no other federated search solution on the market today.
As a start-up with limited resources to devote to R&D, Ontoforce connected with iMinds’ IDLab for help reinventing the search paradigm by developing a federated search solution. The next challenge was to establish a set of data service endpoints — expanding the engine’s search territory beyond just the public web. Because Ontoforce’s solution targeted the biomedical sector, access to university research databases was key. Harvard’s Eagle-i, together with IDLab’s RML stepped in to help on that front. The DISQOVER platform that Ontoforce jointly developed further with IDLab filters and disambiguates query results to add meaning to the data it serves up to users. If a researcher wants to know what diseases are the subject of phase-three clinical trials in, e.g., California, DISQOVER blazes through the network and isolates exactly that information, presenting it graphically in a clean interface that’s easy to understand and manipulate — along with all the relevant links back to the original data. Even the interface is part of the semantic process, bringing extra meaning to displayed data. The Ontoforce solution underscores the importance of collaboration in innovation. iMinds’ IDLab helped federating the search; Harvard’s Eagle-i with IDLab’s RML ensured the data was 5-star quality; and the DISQOVER platform makes sense of it all, “semantifying” the search for users. As a result of this joint collaboration, Ontoforce’s CEO says DISQOVER can scale like no other federated search solution on the market today.
“They’ve basically been our research department,” Ontoforce CEO says of iMinds. “IDLab has a great network, giving us access to many researchers. It’s amazing to be able to get answers quickly from people who are pioneers in their field.”
Halvade
Whole genome sequencing is the process of determining the complete DNA sequence of an individual and is increasingly adopted in both research and clinical settings. Currently, powerful sequencers are able to generate raw molecular data in less than a day in a very cost-efficient manner. However, post-sequencing computational analysis can easily take up to a week even on a powerful workstation.
In collaboration with Janssen R&D, Intel and imec, iMinds researchers have developed Halvade to significantly reduce the analysis time using computational clusters and parallel computing techniques. Halvade adopts cloud technology (Hadoop) and the MapReduce programming model and is able to process an entire whole genome sequencing sample in less than two hours on a modest cluster (15 nodes, 360 CPU cores). This corresponds to ~200-fold speedups compared to sequential execution and facilitates clinical decision making processes that are time-critical.
Decap et al., Bioinformatics, 2015.
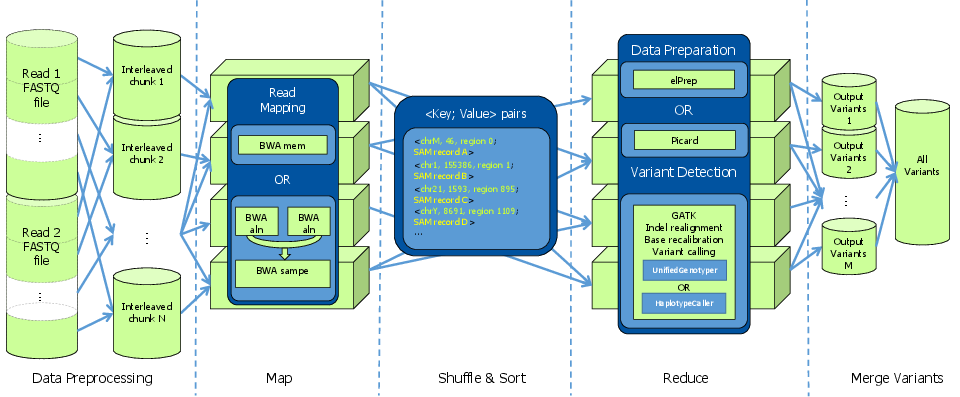
Halvade: parallel post-sequencing analysis using MapReduce
